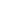Every year, approximately 12 million Americans turn to payday loans as a solution to their short-term financial challenges. For many, these loans become a lifeline during tough times. The payday loan industry can be a lucrative venture for entrepreneurs due to the consistent demand, high-interest rates, and finance charges associated with payday lending.
However, entering this industry requires a solid understanding of its intricacies and a well-thought-out business plan. In this comprehensive guide, we will walk you through the essential steps to become a payday loan lender in the US, while also emphasizing the significance of responsible lending practices and compliance with state regulations. From crafting your business plan to understanding the costs involved, we’ll provide valuable insights into this industry.
What Are The Steps To Becoming a Payday Loan Lender?
Step 1: Register Your Business
If your business is structured as an LLC, it’s essential to have a registered agent within your state before initiating the registration process. In most instances, the overall cost for registering your business typically falls below $300. However, registration fees can vary depending on your specific state regulations and the structure of your business.
The key information you’ll typically need to provide during the registration process includes:
- Business Name: The legal name of your business entity.
- Business Location: The physical address of your business, which can also include a mailing address if applicable.
- Ownership, Management Structure, or Directors: Details about the ownership structure, management team, or board of directors of your business, depending on your business type.
- Registered Agent Information: Information about your registered agent, who will be responsible for receiving legal documents and official correspondence on behalf of your business. This agent must have a physical address within the state of registration.
- Number and Value of Shares (if applicable): If your business is a corporation, you may need to specify the number of shares issued and their respective value.
If you intend to trademark your business name, brand, or product name, you should proceed with trademark registration through the United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) after successfully establishing your business.
For those considering the formation of an S corporation (S corp), the next step is to file Form 2553 with the Internal Revenue Service (IRS). This form is essential for electing S corp status, which provides certain tax benefits and considerations for your business structure.
Step 2: Apply For a State License
Before launching your payday loan website, it’s essential to make sure that you comply with state regulations. Not all states permit payday lending. Some allow payday lending but require lenders to be licensed. The application form will look like this.
In certain states, if a payday loan is made by a business that is not licensed in that state, the payday loan may be void and the borrower will get their money back. Licenses are usually renewed annually.
To register, you must often submit current bank statements that reflect a minimum of $30,000 in liquid assets and $5,000 for each additional physical location, although this will vary by state.
Ensure you are aware of and adhere to these regulations in each state where you plan to offer your services, especially if you are conducting online lending operations across multiple states.
Follow this link to find out about payday lender licenses and requirements in each sate.
Step 3: Open a Transaction Account With Your Bank
To facilitate the lending process efficiently, you’ll need to establish a transaction account with your bank. This account will allow you to conduct electronic funds transfers, enabling you to credit and debit customers’ checking accounts for loan disbursement and repayment.
Work closely with your bank to ensure smooth fund transfers, typically done through the automatic clearinghouse on behalf of the account holder. If you need to, you can work with an attorney to ensure compliance with your state’s rules.
Step 4: Build a Platform
The easier route is to build a payday loan website. However, some payday lenders operate from brick and mortar offices and some are online payday lenders which makes it easier to operate across some of the 37 US states that allow for payday lending. You should check your state’s regulations before committing to either one of these options.
You have an option to build you own tech which can be very customized to your requirements, or you can use an out of the box solution which comes with a CRM to manage all your incoming loan applications. The likelihood is that you will pay a set-up fee to use their software, followed by a monthly fee and this can increased depending on your capacity. Some new companies prefer to use a software to begin and move towards building their own tech over time.
Step 5: Develop a Loan Application Process
Create a loan application process. This should include a way to take down a customer’s details and carry out credit checks, income verification and a clear explanation of the terms and conditions of the loan. Ensure that your application process complies with all applicable laws and regulations.
A software will usually run through thousands of data points to assess a customer’s eligibility for a loan and you will have the option to change the scores according to your risk and number of customers you want to approve and fund. This should be part automated and part manual so your underwriters can review applications and fund those that they would like to.
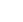
You will need to construct legal terms of your loan agreement (see example below) and this will include all key information including the terms of the loan, fees and interest involved, repayment terms, cancellations, rights and more.
Step 6: Marketing and Customer Acquisition
Develop a marketing strategy to attract borrowers. Consider both online and offline marketing channels, including digital advertising, direct mail, affiliates and search engine marketing. Be transparent about your loan terms and fees in all marketing materials.
Step 7: Risk Management
Make sure you have robust risk management practices to assess and mitigate the risks associated with lending. This includes monitoring loan performance, managing default rates, and adjusting your lending criteria as needed.
Maintain accurate financial records and reports to track your business’s performance. Regularly review your financial statements to ensure your business remains profitable and sustainable.
How Much Does It Cost To Become A Payday Loan Lender?
The cost to become a payday loan lender can vary significantly depending on factors such as the state you operate in, whether you plan to establish a physical storefront or operate online, and the scale of your lending operation. Here are some potential costs to consider:
| Costs | Cost Estimate |
| Licensing Fees | Approximately $150 per year (varies by state) |
| Operating Costs | Rent: $37.83 per sq. ft.
Advertising: 7-8% of budget Loan processing software: $100 per month Website costs: $200 upfront, $50 per month for maintenance |
| Compliance Costs | Legal and regulatory consulting services of $150 to $325 per hour |
| Funding for Loans | Varies depending on state requirements, potentially over $30,000 upfront |
Licensing Fees
State governments typically require payday lenders to obtain licenses, and these licenses may come with associated fees. The cost varies from state to state but can be around $150 each year.
Operating Costs
This includes expenses like:
- Rent (if you have a physical location) – This will depend on your location but the average U.S. office listing rate stands at $37.83 per square foot.
- Advertising – The US Small Business Administration suggests 7-8% of your budget should be spent on advertising.
- Loan processing software – This tends to be around $100 per month.
- Website costs such as domain and site builder fees. – On average, building a website has an upfront cost of around $200 to build a website, with an ongoing cost of around $50 per month to maintain it.
Compliance Costs
Ensuring compliance with state and federal regulations may require legal and regulatory consulting services, which can add to your expenses. Most attorneys charge from $150 to $325 an hour.
Funding for Loans
You’ll need capital to provide loans to customers. The amount will depend on the size and scope of your lending business. Some states require over $30,000 upfront, so be sure to check this before you start.
Do I Need To Be Part Of A Native American Tribe To Become A Payday Loan Lender?
No you do not need to be part of a tribe to become a payday lender. Historically, payday lenders have partnered with tribes attempting to exploit tribal sovereignty as a means to bypass state regulations and usury laws.
Tribes, as sovereign nations, possess legal immunity against certain state laws and regulations. Some payday lenders have partnered with tribes to take advantage of this immunity. This partnership allows the payday lender to claim tribal sovereignty and assert that they are not subject to state usury laws or other regulations that cap interest rates on loans.
In some cases, payday lending companies have claimed to be owned by a Native tribe. However, evidence suggests that the ownership was largely a pretense.
Behind the scenes, the payday lending operation was controlled and managed by the payday lender’s founder, rather than the tribe itself. This arrangement allowed the payday lender to maintain significant control over the lending business while using the tribe’s sovereign status as a shield against legal actions.
Payday lenders operating under this model often charge extremely high-interest rates, well above what is allowed under state laws. This has led to concerns about the predatory nature of such lending practices and their impact on consumers.
In some cases, courts have ruled that the payday lending companies were not genuinely controlled by tribes and, therefore, were not entitled to tribal sovereign immunity. This has led to lawsuits against these lenders for violating state laws. Regulatory actions and lawsuits have put pressure on these lenders to change their practices, often resulting in settlements and modifications to their lending agreements.
By following the steps outlined in this comprehensive guide and considering the additional considerations, aspiring payday lenders can navigate the complexities of the industry, provide a valuable service to those in need of short-term financial assistance, and contribute positively to their communities.
Remember that regulations vary from state to state. Approach this venture with transparency, ethical standards, and a commitment to the financial well-being of your customers.